Introduction
Inflation is an economic notion that refers to a long-term increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. Inflation is commonly represented as an annual percentage rate, which represents the pace at which prices rise over a year.
Inflation is a complicated phenomenon with several causes. Among the most prevalent reasons are:
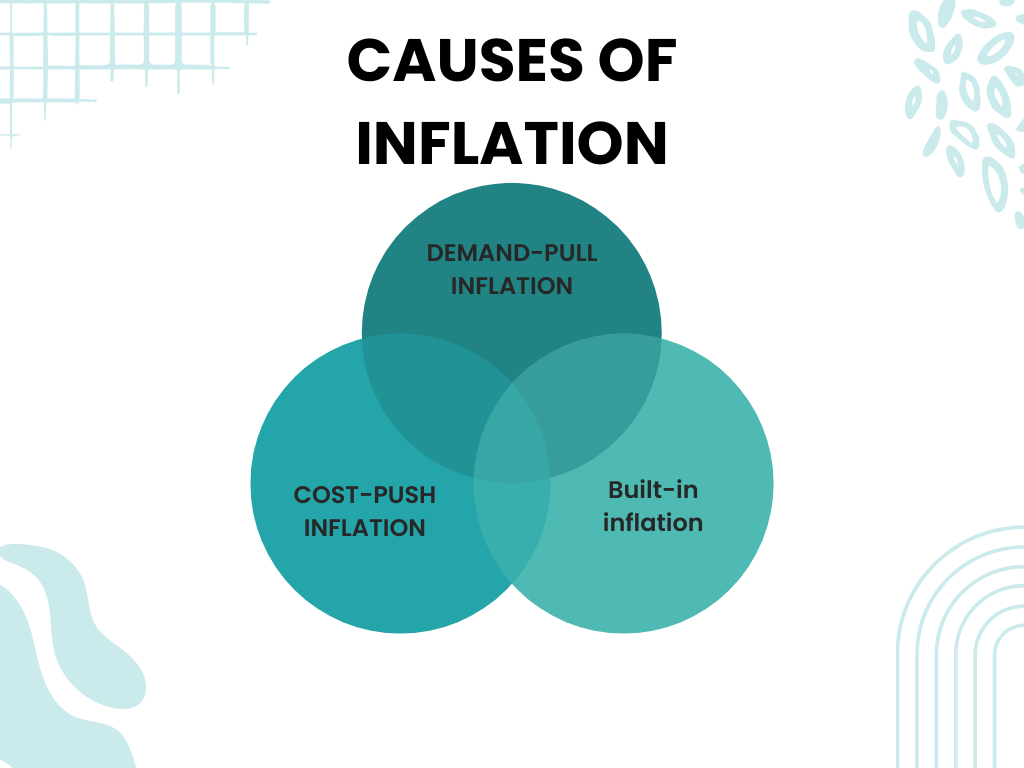
- Demand-pull inflation: It occurs most commonly during periods of considerable economic boom when consumers have greater discretionary income. As a result, consumers increase their spending, increasing demand for products and services. As enterprises boost their prices to match the increasing demand, this increase in demand may exert upward pressure on prices, resulting in inflation.
- Cost-push inflation: Rising production costs, such as higher labor, energy, and raw material costs, produce cost-push inflation. When these expenses rise, firms may feel compelled to pass them on to customers by raising the prices of their goods and services.
- Built-in inflation: Built-in inflation is a type of inflation in which people expect future price rises. This expectation drives people to seek greater pay and anticipate price increases. When firms respond to these demands by raising employee wages and raising pricing, a self-fulfilling loop is created. In other words, when wages and prices continue to rise, the anticipation of increased inflation becomes a reality, resulting in persistent inflationary pressures. Inflation has a number of effects on the economy, both positive and negative.
On the plus side, moderate inflation may stimulate consumption and investment, boosting economic growth. It may also aid in lowering the real value of government debt.
On the other side, rising inflation may diminish people’s and companies’ purchasing power, making it difficult to save for the future. It can also cause economic uncertainty and instability.
To keep inflation under control, central banks frequently utilize monetary policy instruments such as interest rates and asset purchases.
Inflation measurement methods
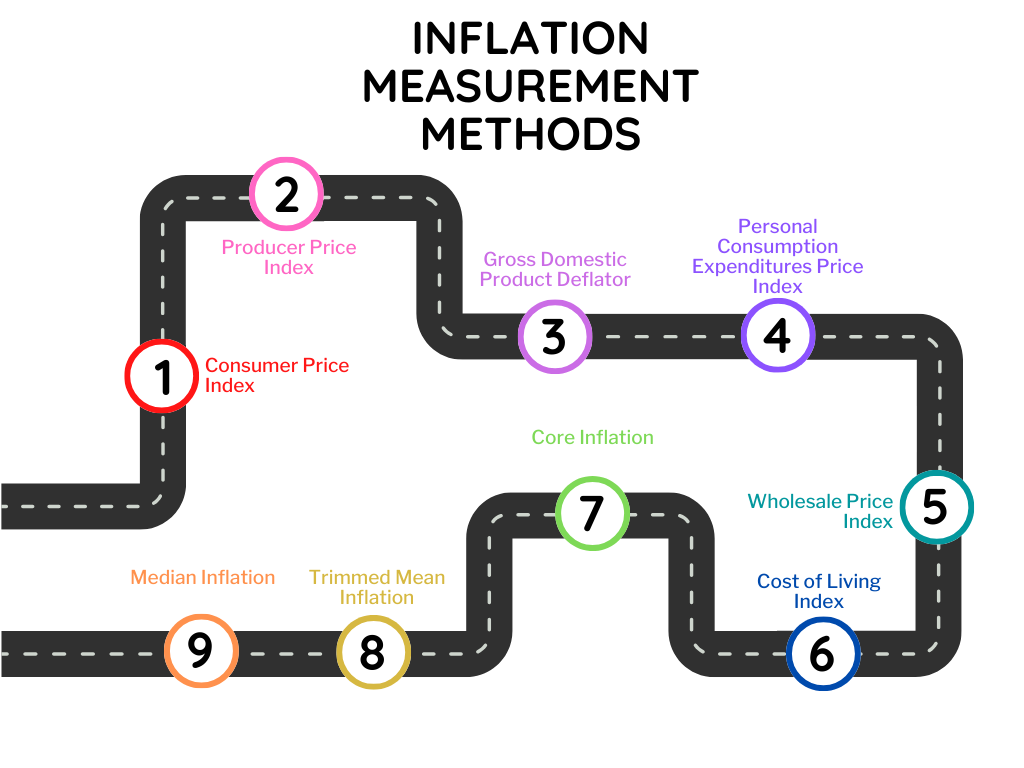

Inflation may be quantified in several ways. The most often used approach is a consumer price index (CPI). A CPI evaluates the prices of a basket of regularly purchased goods and services by households. The consumer price index (CPI) is calculated on a regular basis, and inflation is calculated using the percentage change in the CPI over time.
Another frequent method for measuring inflation is the producer price index (PPI). The PPI is used to calculate wholesale prices for products and services. Because changes in the PPI tend to be reflected later in the CPI, it is typically used as a leading predictor of inflation.
Inflation in Australia
In comparison to many other nations, Australia has a comparatively low inflation rate. The CPI increased by 7.3% in the year to September 2023, the most in 32 years. However, when compared to other nations, such as the United States, where the CPI climbed by 8.5% in the year to July 2023, this is still quite modest.
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) aims for an average inflation rate of 2-3% over time. To keep inflation within this target range, the RBA employs monetary policy instruments such as interest rates.
Impact of Inflation on the Australian economy
Inflation has several effects on the Australian economy.
On the plus side, moderate inflation may stimulate consumption and investment, boosting economic growth. It may also aid in lowering the real value of government debt.
On the other side, rising inflation may diminish people’s and companies’ purchasing power, making it difficult to save for the future. It can also cause economic uncertainty and instability.
How to protect yourself from inflation
There are a number of things that you can do to protect yourself from inflation:
- Invest in assets that tend to appreciate in value during periods of inflation, such as real estate and stocks.
- Invest in index funds that track a basket of stocks, such as the S&P 500.
- Pay down debt as quickly as possible, as the value of debt decreases during periods of inflation.
- Increase your savings rate, so that you have more money to purchase goods and services in the future.
Conclusion
If you are concerned about the impact of inflation on your personal finances, you may take a variety of precautions.
There are a variety of tools accessible to assist you with your macroeconomics assignment. There are several online sites that explain macroeconomic topics and practice issues. You can also seek assistance from your instructor or a tutor.
If you need help with a macroeconomics assignment, there are a number of resources available to you. You can get help from your teacher or from a tutor. You can also find online resources that provide help with macroeconomics assignments.
Are you prepared to thrive in macroeconomics? Contact Assignment Unlocked immediately for superior macroeconomics assignment assistance and unleash your academic potential!






