The deadly but treatable disorder known as rheumatic heart disease (often abbreviated as RHD) still affects communities, especially those of Australia’s Indigenous peoples. If not identified and treated in its early stages, this inflammatory heart condition, which frequently develops from untreated streptococcal infections, can cause serious problems. We will examine the symptoms of rheumatic heart disease (RHD) in this extensive guide to better help you comprehend this ailment, its repercussions, and the value of early identification.
Rheumatic Heart Disease
Rheumatic fever, which is brought on by certain strains of the Group A Streptococcus bacteria, can lead to rheumatic heart disease, a chronic ailment. RHD may result from heart valve disease brought on by rheumatic fever. As a result of this illness, which predominantly affects the heart’s valves, the heart’s ability to pump blood might be permanently damaged.
Signs and Symptoms of Rheumatic Heart Disease
RHD can present with a variety of symptoms that might vary from person to person. Recognising these symptoms is crucial since early intervention and severe cardiac damage can be avoided with early identification. The main warning signs and symptoms of rheumatic heart disease are as follows:
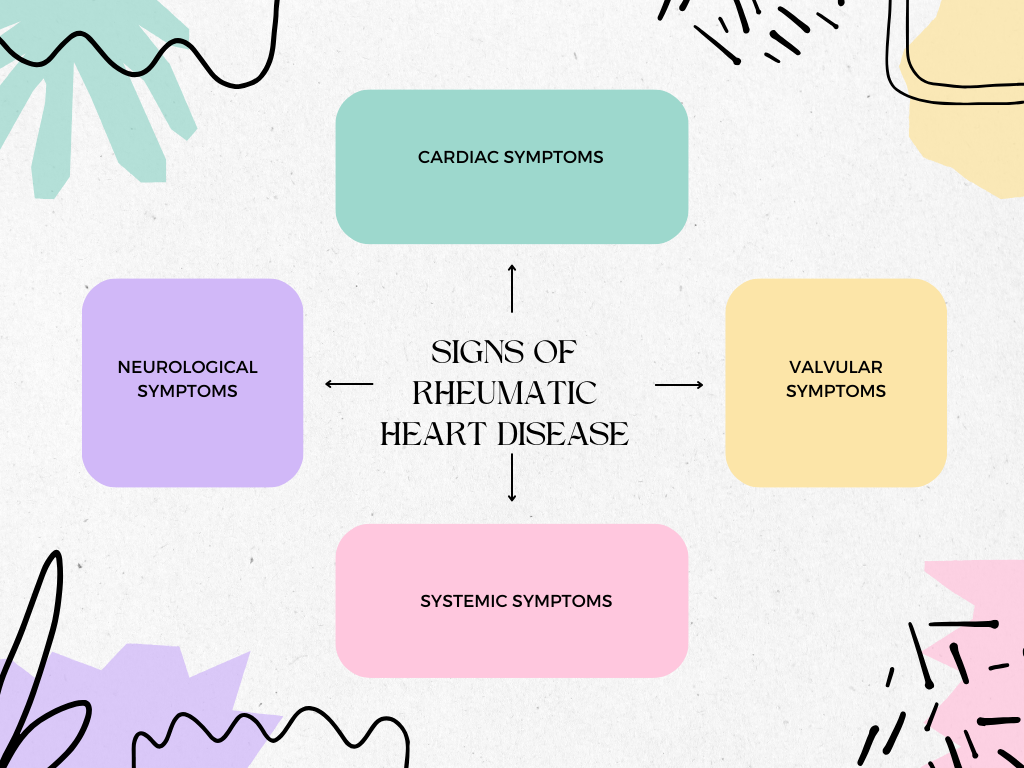
I. Cardiac Symptoms
- Chest Pain and Discomfort: Chest pain or discomfort, frequently characterized as a dull aching or pressure in the chest, is one of the defining symptoms of RHD. Although this symptom may come and go, it should never be disregarded.
Palpitations: RHD can be identified by irregular heartbeats or palpitations, which are symptoms of damaged heart valves that impair the heart’s capacity to pump blood efficiently.
Shortness of Breath: Shortness of breath may develop when RHD worsens, especially during vigorous exercise or when lying down.
II. Valvular Symptoms
- Heart Murmurs: Unusual noises made by the heart are known as murmurs. Damaged heart valves in RHD can result in turbulent blood flow, which can be heard as heart murmurs by a medical professional doing a physical examination.
- Fatigue: RHD is frequently characterized by persistent weakness and weariness, which are frequently brought on by the heart’s ineffectiveness in pumping blood.
III. Systemic Symptoms
- Fever: High fever is a common symptom of rheumatic fever, which can cause RHD. Fever is a warning sign for future rheumatic heart disease development, even if it may not always be the case. This is especially true if it is present together with other symptoms.
- Joint Pain and Swelling: Particularly in the bigger joints, such as the knees and elbows, rheumatic fever can induce joint inflammation and discomfort.
- Skin Rashes: RHD patients can get skin rashes that appear as red, elevated, and asymmetrical areas.
IV. Neurological Symptoms
- Sydenham’s Chorea: Sydenham’s chorea, a neurological condition characterized by uncontrollable muscular movements, mental instability, and behavioral disturbances, can occasionally result from RHD.
It’s crucial to remember that RHD symptoms may not appear right away following a case of rheumatic fever or streptococcal infection. In actuality, symptoms could not appear for years or even decades, so early identification and consistent follow-ups are essential, especially for individuals who are at risk.
Who is at Risk for Rheumatic Heart Disease?
RHD is more prevalent in certain populations and age groups. The risk factors include:
- Age: RHD is most commonly diagnosed in children and young adults, typically between the ages of 5 and 15.
- Geography: Indigenous communities, particularly in Australia, have a higher prevalence of RHD. Access to healthcare, socioeconomic factors, and living conditions can influence the risk.
- History of Rheumatic Fever: Individuals who have previously had rheumatic fever are at a higher risk of developing RHD.
Preventing Rheumatic Heart Disease
Prevention is the key to reducing the burden of RHD. Effective prevention strategies include:
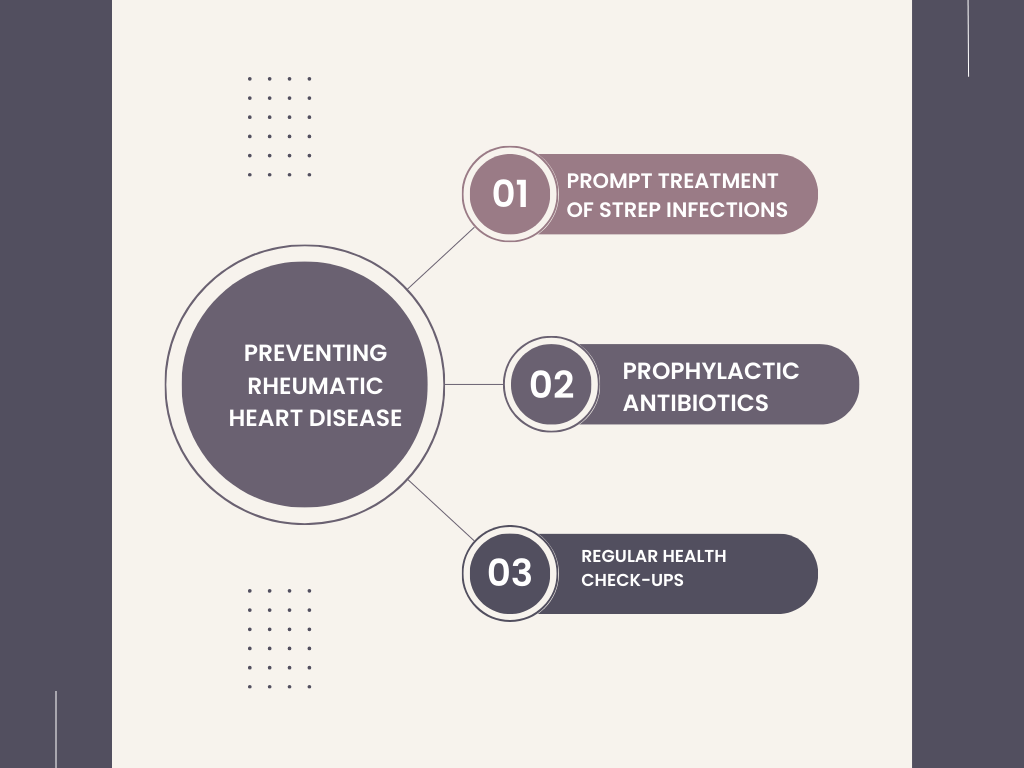
- Prompt Treatment of Strep Infections: Treating streptococcal infections, especially in children, can prevent the development of rheumatic fever and, subsequently, RHD.
- Prophylactic Antibiotics: For individuals at risk of RHD, such as those with a history of rheumatic fever, prophylactic antibiotics can help prevent further streptococcal infections.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Individuals at risk should have regular check-ups to detect RHD in its early stages.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the signs and symptoms of rheumatic heart disease is crucial for early detection and management. With a higher prevalence in certain communities, particularly among Indigenous populations in Australia, recognizing the indicators of RHD is of utmost importance.
If you or a loved one shows any of the signs and symptoms mentioned in this article, seek immediate medical attention. Early intervention can help prevent further heart valve damage and improve long-term outcomes.
Remember, awareness and education about RHD are essential. The fight against this preventable heart condition begins with knowledge, proactive healthcare, and community support.