Unemployment is defined as being out of work unwillingly. It is a big economic and social issue with serious consequences for people, families, and communities.
There are three main types of unemployment:
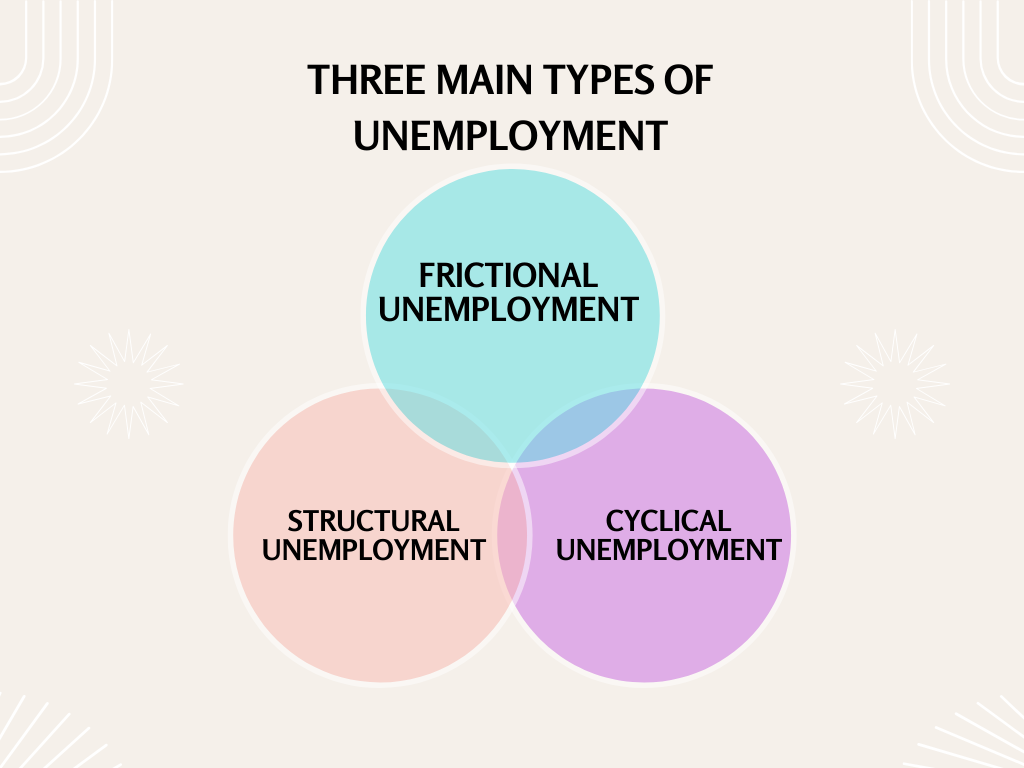
- Frictional unemployment: This is the form of unemployment that arises when people are in between jobs over an extended period of time. Workers moving from one job to another is a normal component of a functioning economy.
- Structural unemployment: When there is a mismatch between the skills necessary for available occupations and the skills of the workforce, this sort of unemployment develops. This might be because of technical advancements, globalization, or other considerations.
- Cyclical unemployment: This type of unemployment occurs during economic downturns. It is caused by a decline in aggregate demand, which forces enterprises to reduce output and lay off workers. This sort of unemployment reflects the business cycle and is more prevalent during recessions.
Addressing each type often requires different strategies and interventions to help individuals find employment and ensure the stability of the job market.
Frictional unemployment
As people shift from one job to another, this is a normal component of the economy. It can be caused by a number of circumstances, including:
- Job search: Workers may be out of work for a short time while looking for new employment.
- Seasonal employment: Some employees, such as construction workers in the winter, may be unemployed during specific seasons of the year.
- Quitting a job: Some employees may willingly leave their positions, for example, to explore a new opportunity or to take a break from work.
Frictional unemployment is often short-term, with most people finding new jobs within a few weeks or months. However, frictional unemployment can still have a detrimental impact on workers since they may lose income and benefits while out of work.
Structural unemployment
The problem of structural unemployment is more significant than the problem of frictional unemployment. It happens when there is a mismatch between the skills necessary for available employment and the workforce’s talents. This might be attributed to a number of circumstances, including:
- Technological change: Jobs can become outdated as a result of technological advancement. ATMs, for example, resulted in the loss of thousands of bank teller positions.
- Globalization: Jobs may be relocated overseas due to globalization, where labor costs are cheaper. Many manufacturing employment, for example, has shifted from developed to emerging countries in recent decades.
- Government policy: Government policy can also have an impact on structural unemployment. Trade restrictions, for example, might make it harder for domestic enterprises to compete with foreign businesses, resulting in job losses.
Addressing structural unemployment may be challenging and time-consuming. Workers may need to retrain in order to gain the skills required for available employment. It may also necessitate government engagement, such as trade programs, to assist firms in competing on a worldwide scale.
Cyclical unemployment
Depending on the intensity of the economic slump, cyclical unemployment can be severe and long-lasting. The Great Recession of 2008-2009, for example, resulted in a dramatic increase in unemployment rates in several nations.
Typically, cyclical unemployment is handled by macroeconomic measures such as fiscal and monetary policy. Fiscal policy may be used to raise government spending while decreasing taxes, increasing aggregate demand, and creating jobs. Monetary policy may be used to cut interest rates, making it less expensive for firms to borrow and invest.
Impact of unemployment on the job market
Unemployment has a significant negative impact on the job market. It can lead to:

- Lower wages: Workers have less negotiating leverage when unemployment is high, and they may be compelled to accept lower salaries.
- Fewer job opportunities: There are fewer job prospects accessible when organizations lay off employees. Job seekers may find it more difficult to find work as a result of this.
- Discouragement: After being unemployed for an extended length of time, some job searchers may feel disheartened. This may cause people to abandon their job hunt and exit the workforce.
Unemployment may also have a detrimental influence on the economy as a whole. It has the potential to reduce consumer spending and investment, slowing economic development even more.
Conclusion
Unemployment is a complicated problem with no simple answers. However, understanding the many forms of unemployment and their causes is critical in order to establish effective strategies to solve them.
There are a variety of tools accessible to assist you with your macroeconomics assignment. You may either ask your teacher for assistance or seek tutoring. There are also other online resources that might assist you with your macroeconomics assignments.
Are you prepared to thrive in macroeconomics? Contact Assignment Unlocked immediately for superior macroeconomics assignment assistance and unleash your academic potential!